- Head Office
- #2026, SpaceOn Knowledge Industry Center, 51-25 Manseongbuk-ro, Deokjin-gu, Jeonju-si, Jeollabuk-do, Korea
- TEL
- +82-63-270-3998
- FAX
- +82-63-000-0000
- biorheologics7@naver.com
Copyright ⓒbiorheologics. All rights reserved.
OVERVIEW
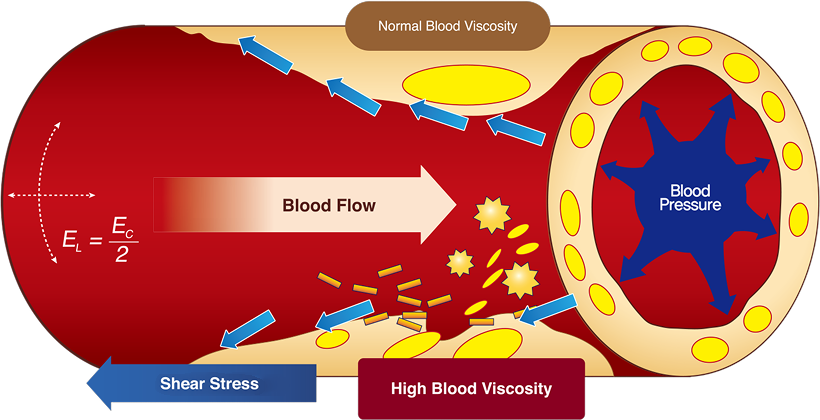
The higher the viscosity, the slower the blood flow becomes, which in turn hampers smooth circulation and disrupts the delivery of oxygen and nutrients.
Units are expressed as (mP, cP, mPa·s), representing the degree of difficulty blood faces when passing through the inner walls of blood vessels.
(KFDA Medical Device Classification: KFDA – Class 1 A22240.01(1))
HEMODYNAMICS